 Figure 1. Slingboxes sit on the TV and connect wirelessly to a computer or mobile device. Photo from http://us.slingmedia.com/page/statichome. |
 Figure 1. Slingboxes sit on the TV and connect wirelessly to a computer or mobile device. Photo from http://us.slingmedia.com/page/statichome. |
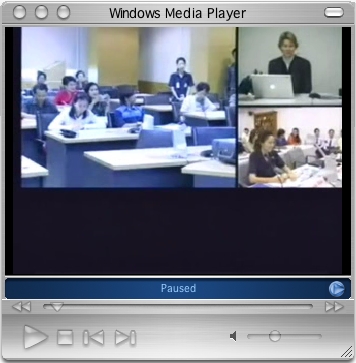 Figure 2. Leslie Opp-Beckman (top right), as seen video conferencing on the Web from the University of Oregon to two locations in Thailand (left and bottom right). The video recording of the event becomes a reusable learning object. http://thaiuo.uoregon.edu/session_01.html. (© 2005 Copyright American English Institute and CET Interactive Media.) |
| The
project we are doing is an amazing idea in order to learn the
language in another way. To my mind, that’s very important to know to
how to communicate correctly in English with other people, especially
if they are from abroad. This opportunity[talking via Skype] that we
had was a perfect
occasion to do it! We were able to do something that, I think, not many students would ever do. Luckily, I and my classmates could do it! We talked with Spanish students from the USA. We exchanged opinions about many different and interesting topics. |
74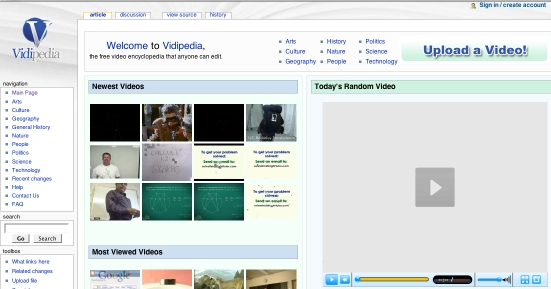 |
|
Figure
3. Vidipedia's
front page has an alphabetized list of topics (upper left), and also allows for
tagging that links to related articles. http://www.vidipedia.org/Main_Page.
(GNU FDL).
|
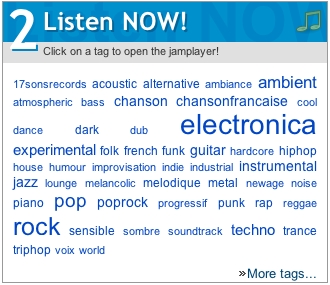 |
| Figure
4. jamendo
demonstrates the number of matches to their
database by the size of the producer-defined tag. http://www.jamendo.com/. |